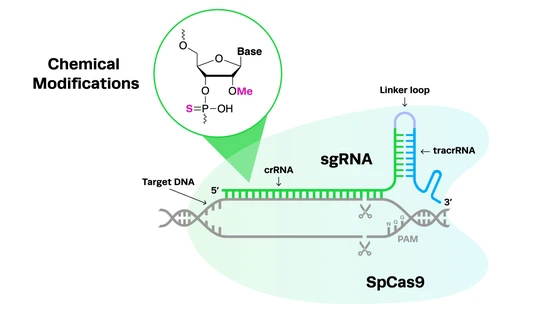
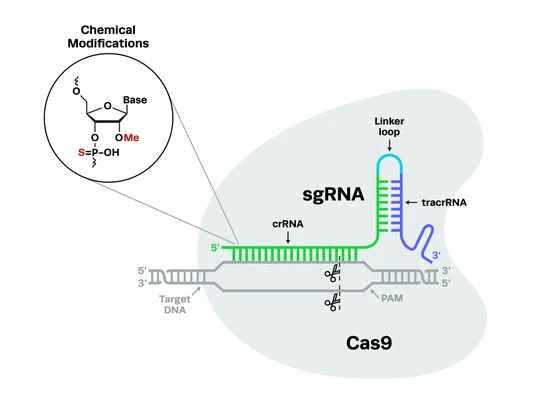
Bioenergy is a promising solution to the world’s energy crisis. Plant & animal by-products can be a useful resource for the generation of energy. Biofuels can even be generated from organisms such as algae and bacteria. However, to produce commercially viable amounts of biofuel is a huge challenge.
CRISPR is a remarkable genome editing tool that has been revolutionizing research in every industry, and bioenergy is no exception. The recent advances in CRISPR indicate that perhaps this technology may save the day by offering a solution to the energy crisis in the future.
In this post, we will discuss the basic concepts of what bioenergy is and how CRISPR is being used in this area. Specifically, we will cover:
What is Bioenergy?
Bioenergy is renewable energy generated from natural sources. The sources include plants, animals, and their byproducts. Bioenergy is suitable to help solve the world’s energy crisis, as it is a sustainable power source; energy contained in plants is obtained from the sun—an inexhaustible energy source.
What is Biomass and How Does It Generate Energy?
Biomass is a renewable energy source that typically consists of organic matter: wood, by-products of agricultural and forestry processes, organic industrial, animal, and human wastes. Biomass contains stored energy originally obtained from the sun; when biomass is burned, the chemical energy contained is released as heat (energy).
The three ways by which energy can be generated from biomass are:
- Direct burning: Solid biomass materials can be burned directly to produce heat. This heat is used to generate steam, which is then sent through a steam turbine to generate electricity.
- Conversion to biogas: Methane is obtained from wet biomass when it undergoes fermentation whereas synthesis gas (syngas) is produced by subjecting dry biomass to high temperatures in the absence of oxygen.
- Conversion to biofuel: Biomass can be directly converted into fuel cells and these are known as biofuels.
Biofuels: What Are They and Why Do We Need Them?

Biofuel is the combustible fuel obtained from biomass, and are either first or second generation biofuels. First generation biofuels are unprocessed organic materials such as wood chips & pellets used for cooking or generating electricity. Second generation biofuels are processed and liquified and include ethanol and biodiesel.
Biofuel production: how is it made?Biofuel is produced either through a fermentation process, or a chemical reaction. The type of biofuel produced depends on the processing of the biomass. For example, ethanol is a by-product of the fermentation processes of plant sugars whereas biodiesel is produced as a result of a chemical reaction between greases with alcohol.
Recently, scientists have used a novel approach of tweaking bacteria and algae using CRISPR to produce biofuels. With this process, CRISPR is adding to the uses of biofuels, and radically transforming the energy sector!
Biofuel is produced either through a fermentation process, or a chemical reaction. The type of biofuel produced depends on the processing of the biomass. For example, ethanol is a by-product of the fermentation processes of plant sugars whereas biodiesel is produced as a result of a chemical reaction between greases with alcohol.
Recently, scientists have used a novel approach of tweaking bacteria and algae using CRISPR to produce biofuels. With this process, CRISPR is adding to the uses of biofuels, and radically transforming the energy sector!
How CRISPR and Biofuel Can Solve the Energy Crisis
We now have a third generation biofuel generated from tiny organisms such as bacteria & algae. While previous studies had laid the foundation of this field, the addition of CRISPR gene-editing to the biotechnologists’ toolbox has further accelerated the research on biofuel generation using microbes.
CRISPR used to generate biofuel from algaeCRISPR has made it possible to produce double the amount of biodiesel from phototropic algae—a concept that scientists have been attempting to optimize since the 1970s. A team of researchers from California have found a way of doubling the lipid production in algae, using CRISPR to tweak the genes.
CRISPR has made it possible to produce double the amount of biodiesel from phototropic algae—a concept that scientists have been attempting to optimize since the 1970s. A team of researchers from California have found a way of doubling the lipid production in algae, using CRISPR to tweak the genes.
Algae are tiny, slimy organisms that reek of fish! These organisms, like plants, need sunlight, carbon dioxide, and other nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus to survive. If you put them on an extreme diet (starve them of the essential nutrients), they start storing energy.
Instead of growing and multiplying, they become sluggish, go into a dormant stage, and start building up fatty lipids. Scientists identified 20 transcription factors that regulate lipid production in algae. They then used CRISPR to knock out 18 of these, and were able to double the lipid production in algae.
This research was a collaboration between companies ExxonMobil and Synthetic Genomics, both aiming to advance biofuel energy research. The companies recently announced that a new phase of their research program could lead to the generation of 10,000 barrels of algae biofuel per day by 2025!
CRISPR protects yeast from damage in biofuel productionYeast are powerful model organisms often used in industrial production. However, the stress of excessive protein or metabolite generation impacts the organisms during the bioproduction cycle. Pre-treatment chemicals that are used to speed up the process of cellulose breakdown into sugars are also potentially harmful to yeast.
Yeast plays an important role in the fermentation of the sugars to biofuels. Researchers have now found a way to protect yeast from damage during the biofuel production process using CRISPR. The research team made two changes to a single gene such that yeast is now tolerant to these pre-treatment chemicals!
Yeast are powerful model organisms often used in industrial production. However, the stress of excessive protein or metabolite generation impacts the organisms during the bioproduction cycle. Pre-treatment chemicals that are used to speed up the process of cellulose breakdown into sugars are also potentially harmful to yeast.
Yeast plays an important role in the fermentation of the sugars to biofuels. Researchers have now found a way to protect yeast from damage during the biofuel production process using CRISPR. The research team made two changes to a single gene such that yeast is now tolerant to these pre-treatment chemicals!
CRISPR acts as a gene-editing tool for acetogenic bacteriaClostridium autoethanogenum is an acetogenic microbe used for gas fermentation. This tiny organism can be used for the commercial scale production of ethanol. However, commercial exploitation of acetogenic microbes is challenging, as scientists only have a basic understanding of it, and there is limited availability of genetic tools and high-throughput engineering platforms. In a recent study, CRISPR has shown improved efficiency of gene-deletion in this bacteria, making it a viable tool for engineering this tiny organism!
Clostridium autoethanogenum is an acetogenic microbe used for gas fermentation. This tiny organism can be used for the commercial scale production of ethanol. However, commercial exploitation of acetogenic microbes is challenging, as scientists only have a basic understanding of it, and there is limited availability of genetic tools and high-throughput engineering platforms. In a recent study, CRISPR has shown improved efficiency of gene-deletion in this bacteria, making it a viable tool for engineering this tiny organism!
Energy Crisis? CRISPR to the Rescue!
Greenhouse gases are released during the combustion of fossil fuels, and is one of the leading contributing factors causing global warming. An alternate source of energy is desperately needed and energy biotechnology offers a promising solution.
Currently, bioenergy can meet only 10% of the world’s energy demand. Further technology is needed to produce commercially viable amounts biofuels, and CRISPR has already proven that it can help. With further refinement of CRISPR technology and more and more companies investing in CRISPR-based bioenergy research, we can dream of potentially ending the world’s energy crisis in the future.
If you are interested in keeping up with the latest CRISPR trends, be sure to subscribe to our blog or follow us on Twitter or Facebook!